The Stages of Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary issues progress over time in stages. Understanding these stages is crucial to identifying the condition early and taking necessary action before it causes significant harm to your heart. Here’s how CAD develops:
Early Stage: Plaque Formation
In the early stages, “plaque – a mixture of fat, cholesterol, and other substances” – begins to form inside the walls of the coronary arteries. This process, known as atherosclerosis, doesn’t usually cause noticeable symptoms, but the arteries slowly begin to narrow. While the blockage is minor, blood flow is still relatively normal.
Intermediate Stage: Narrowed Arteries and Reduced Blood Flow
As plaque builds up, the arteries continue to narrow, reducing the blood flow to the heart. This can lead to angina (chest pain) and other symptoms like shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or stress. The heart may not get enough oxygen, causing discomfort or fatigue.
Advanced Stage: Severe Blockage and Heart Attack Risk
In the advanced stage, plaque can completely block one or more of the coronary arteries, leading to severe restricted blood flow to the heart. This is when the risk of a heart attack becomes significant.
!!!!If a blood clot forms around the plaque, it can completely block the artery, preventing oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart muscle, which can lead to tissue damage or death.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can develop gradually, and in the early stages, many people may not notice any symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, certain signs and symptoms may start to appear. Here are the common symptoms of CAD:
- Chest Pain (Angina)
- Shortness of Breath
- Feeling unusually tired or weak, even after a full night’s sleep
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness
- Swelling in the Legs, Ankles, or Feet=
- Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia)
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking medical attention before the condition worsens is important. Early detection and intervention can prevent severe complications like heart attacks or heart failure, improving long-term heart health. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is primarily caused by a combination of lifestyle factors and health conditions. Here are the most common causes and risk factors for CAD:
- Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol)
- Smoking
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
- Diabetes
- Poor Diet
- Lack of Physical Activity
- Stress
- A family history of heart disease can increase your risk, as genetics can play a significant role in developing coronary artery issues.
By understanding these causes and risk factors, you can make informed decisions about lifestyle changes and treatments to reduce your risk of CAD and protect your heart health.
Can Coronary Artery Issues Cause Heart Attack?
 Yes, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can lead to a heart attack. Here’s how:
Yes, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can lead to a heart attack. Here’s how:
- Plaque Buildup: Over time, plaque made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances forms inside the coronary arteries. This causes the arteries to narrow and restrict blood flow to the heart.
- Plaque Burst: If the plaque bursts, it can trigger the formation of a blood clot around the ruptured plaque.
- Blockage of Arteries: The blood clot can block the artery completely, preventing oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart muscle.
- Heart Muscle Damage: When the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen, it can suffer damage or even die. This is what leads to a heart attack.
- Importance of Timely Intervention: Early detection and timely intervention are crucial in preventing a heart attack. Managing risk factors like high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes can help prevent CAD from progressing to this point.
If you experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, seek medical help immediately to reduce the risk of serious heart damage. Regular check-ups and screenings are vital for early detection and prevention.
Treatment Options for Coronary Heart Disease

There are several treatment options available for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), depending on the severity of the condition. These treatments aim to manage symptoms, reduce risks, and improve blood flow to the heart. Here are the main treatment options:
Lifestyle Changes
- Dietary Modifications: Eating a heart-healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, helps lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves circulation, helping to manage CAD.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels, and quitting is essential for reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can help manage heart health.
Medications
- Statins: Used to lower cholesterol levels and reduce plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Blood Pressure Medications: ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers help manage high blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Medications like aspirin or clopidogrel reduce blood clot formation, helping to prevent heart attacks.
- Diabetes Medication: For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is critical to prevent further damage to blood vessels.
Angioplasty and Stenting
- Angioplasty: This procedure involves inserting a small balloon into the blocked artery and inflating it to widen the artery, improving blood flow.
- Stenting: After angioplasty, a small metal mesh tube (stent) is placed in the artery to keep it open, preventing future blockages.
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG)
- Bypass Surgery: In more severe cases of CAD, surgery may be necessary to bypass the blocked arteries using healthy blood vessels taken from another part of the body. This improves blood flow to the heart and reduces the risk of a heart attack.
- When It’s Needed: CABG is typically recommended for patients with multiple blocked arteries or for those whose blockages cannot be treated with angioplasty.
Cardiac Rehabilitation
- After medical or surgical treatment, cardiac rehabilitation programs are often recommended. These programs involve supervised exercise, counseling, and education to improve heart health and support recovery.
Each treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease. For mild cases, lifestyle changes and medications may be enough. However, for more advanced stages, procedures like angioplasty, stenting, or even bypass surgery might be necessary to restore normal heart function and prevent complications. Always consult a cardiologist to choose the best treatment based on individual needs.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) or is concerned about heart health, it’s important to seek professional help. Consult with top cardiologists and get a personalized treatment plan. Click the button below to schedule a free consultation today and take the first step toward a healthier heart!
Consult Online Cardiologist
Conclusion
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can be a serious condition, but with early detection and treatment, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications like heart attacks or heart failure. Whether through lifestyle changes, medications, or more advanced procedures, managing CAD is key to maintaining a healthy heart.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of CAD or want to get ahead of potential heart problems, don’t wait. Get connected with a cardiologist today to discuss your concerns and explore the best treatment options for your heart health.
Visit MantraDoc to get connected with an expert cardiologist and take charge of your heart health now!
 “Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a condition that occurs when the coronary arteries—the blood vessels responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to your heart—become narrowed or blocked”
“Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a condition that occurs when the coronary arteries—the blood vessels responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to your heart—become narrowed or blocked”
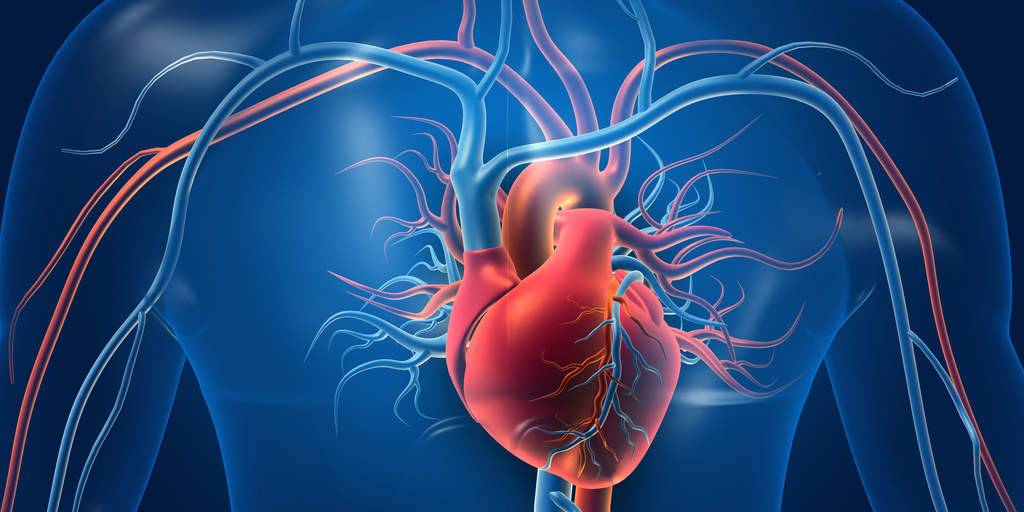

 Yes, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can lead to a heart attack. Here’s how:
Yes, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) can lead to a heart attack. Here’s how: