Do you often feel discomfort or pain in your back that just doesn’t seem to go away, especially after sitting for a long time or during certain movements? If you’re experiencing stiffness, limited mobility, or pain that worsens with activity, it could be a sign of spinal arthritis—a condition that affects millions of people, especially as we age.
While it’s true that it can be challenging to live with, many people with this condition continue to live full, active lives with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments. In this blog, we’ll explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available for managing spinal arthritis.
Contents
- 1 What is Spinal Arthritis?
- 2 Common Causes and Risk Factors for Spinal Arthritis
- 3 Symptoms of Spinal Arthritis You Should Watch Out For
- 4 How Spinal Arthritis Is Diagnosed
- 5 How to Manage Spinal Arthritis Pain at Home
- 6 Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Spinal Arthritis
- 7 When to See a Specialist for Spinal Arthritis
What is Spinal Arthritis?
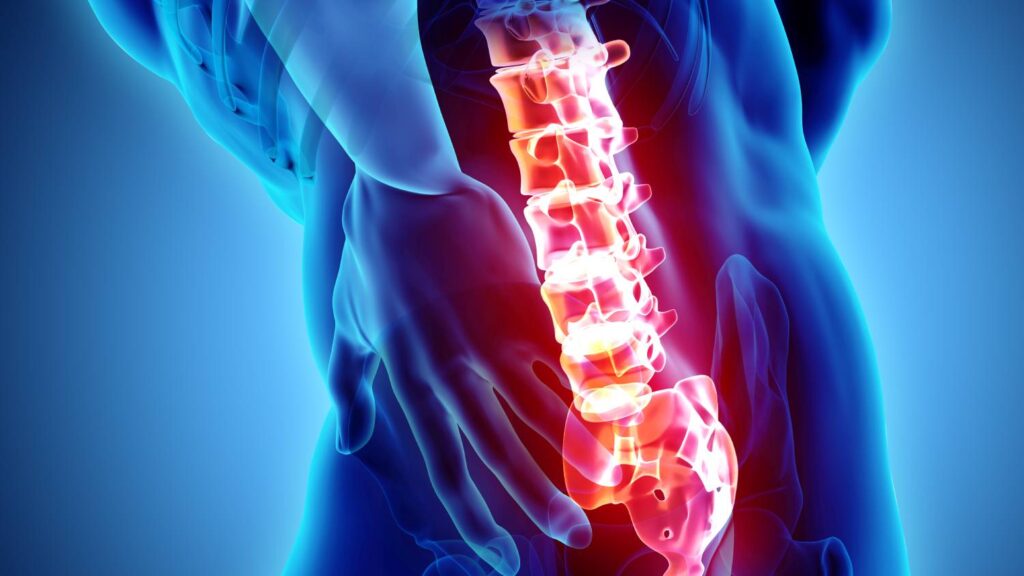
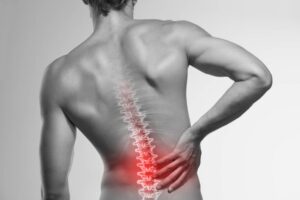 Spinal arthritis, also known as spondylosis or arthritis of the spine, refers to the degeneration of the joints and discs in the spine. It happens when the cartilage that cushions the bones in the spine begins to break down, leading to bone spurs and inflammation. This condition is commonly associated with aging, but it can also be caused by injury, repetitive stress, or genetic factors.
Spinal arthritis, also known as spondylosis or arthritis of the spine, refers to the degeneration of the joints and discs in the spine. It happens when the cartilage that cushions the bones in the spine begins to break down, leading to bone spurs and inflammation. This condition is commonly associated with aging, but it can also be caused by injury, repetitive stress, or genetic factors.
In spinal arthritis, the intervertebral discs (the cushions between the bones) lose their flexibility, and the joint spaces narrow. As a result, the bones may rub together, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness in the spine. This leads to reduced mobility and discomfort, especially after prolonged periods of sitting, standing, or bending.
How It Affects the Spine:
- Pain: The breakdown of cartilage can cause inflammation, leading to pain, especially in the lower back or neck.
- Stiffness: Spinal arthritis can make it harder to bend, twist, or even sit comfortably for long periods.
- Reduced Mobility: As the condition worsens, you may find it difficult to move freely or perform routine tasks without pain or discomfort.
While spinal arthritis can affect any part of the spine, it most commonly occurs in the lower back (lumbar spine) or the neck (cervical spine). Over time, it can significantly impact your quality of life, but with proper management, the symptoms can be alleviated, and mobility can be improved.
Common Causes and Risk Factors for Spinal Arthritis
 Spinal arthritis, like many degenerative conditions, develops over time due to a variety of factors. Here are the most common causes and risk factors that contribute to the development of spinal arthritis:
Spinal arthritis, like many degenerative conditions, develops over time due to a variety of factors. Here are the most common causes and risk factors that contribute to the development of spinal arthritis:
-
Age
As we get older, the cartilage in the spine naturally wears down due to years of use and wear. This makes older adults more susceptible to developing the condition, particularly after the age of 50. -
Injury
Previous spinal injuries, such as fractures, sprains, or herniated discs, can increase the risk of spinal arthritis. -
Genetics
A family history of spinal arthritis or other joint conditions can increase your risk of developing the disease. -
Obesity
Carrying extra weight puts added stress on the spine, especially on the lower back. -
Poor Posture and Repetitive Stress
Poor posture or repetitive activities that involve heavy lifting, bending, or twisting can put excessive stress on the spine, increasing the risk of injury and cartilage breakdown. -
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to weakened muscles and poor spinal health. -
Occupational Hazards
Jobs that require heavy lifting or repetitive movement can strain the spine and increase the risk of arthritis over time.
By understanding these risk factors, you can take proactive steps to minimize your risk of spinal arthritis before the condition worsens.
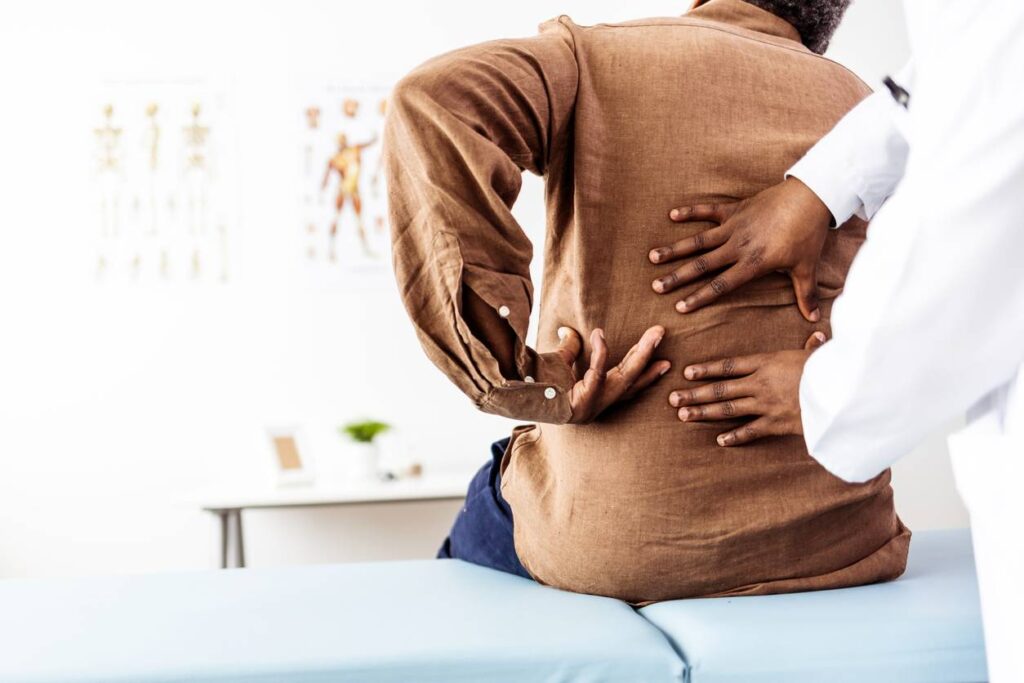
Symptoms of Spinal Arthritis You Should Watch Out For
 If you’re dealing with spinal arthritis, you may experience the following symptoms:
If you’re dealing with spinal arthritis, you may experience the following symptoms:
- A dull or aching pain in the lower back or neck that worsens with movement or after long periods of sitting or standing.
- Stiffness in the Spine
- Trouble performing basic tasks like bending down, standing up, or turning your head due to stiffness or pain in the spine.
- A feeling of numbness or tingling in the arms or legs
- A sensation or sound of creaking or popping when moving the spine, caused by the rubbing of bones due to cartilage loss.
- Muscle weakness
- Pain that travels to other parts of the body, such as the hips, legs, or arms, especially if the arthritis affects the nerves.
- Increased pain with activity
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to manage the condition and prevent further damage. Early diagnosis can help you take appropriate action to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility.